What is Blue Mind Theory?

Blue Daily
| 3 min read

Water in the ocean, rivers, lakes and even baths can make us feel calmer, increase well-being and boost creativity. Blue Mind is the mildly meditative state people fall into when they are near, in, under or on water. Here's everything you need to know about the science behind water's meditative properties.
What is Blue Mind?
Water positively affects the mind and body, and the Blue Mind Theory — also known as "the Blue Water Theory" or simply "Blue Mind" — provides ways people can use water to improve their well-being.
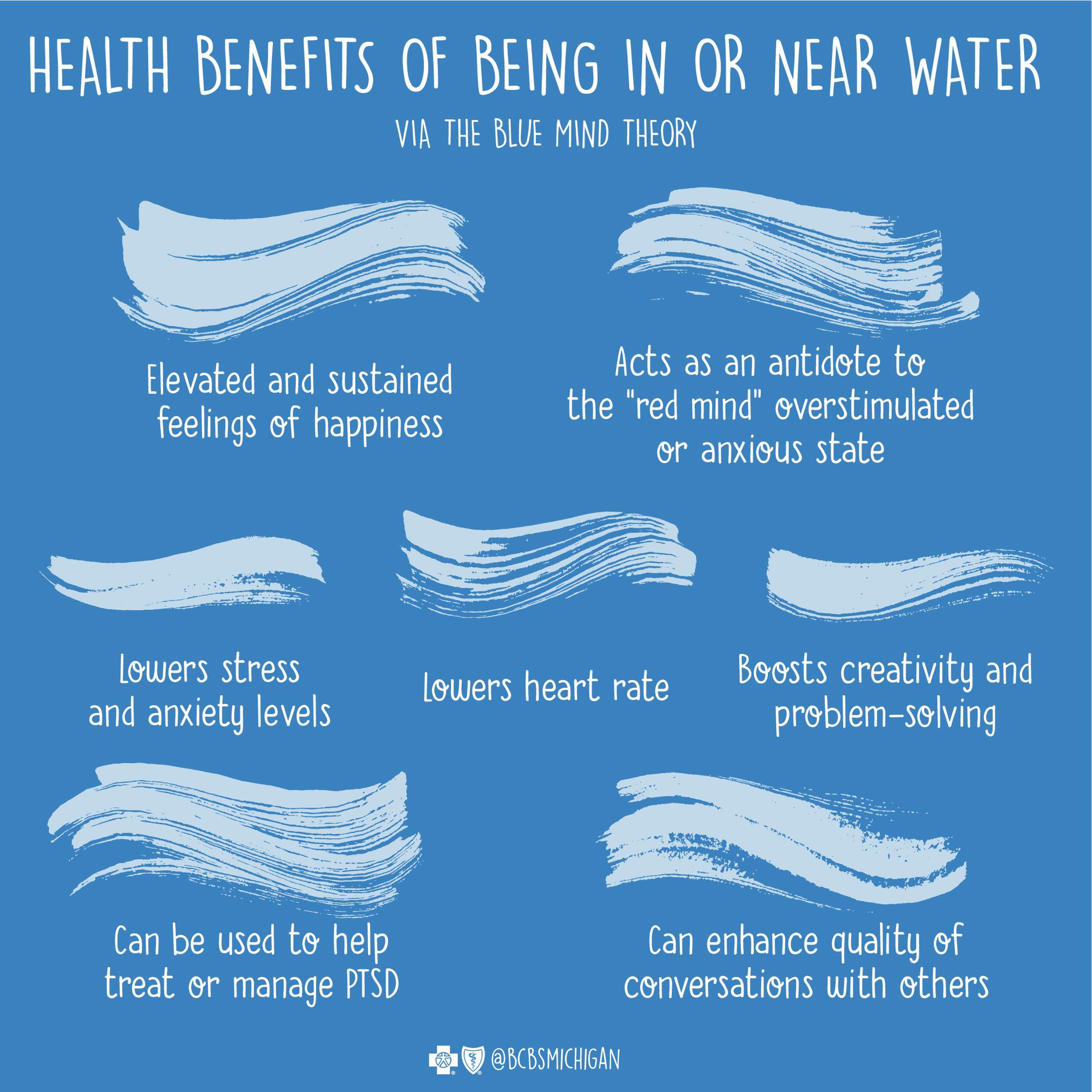
The blue mind effect can be described as a state of water-associated peace. Some of the ways water can produce physical and mental health benefits include:
- Bodies of water trigger involuntary attention, which is essential to problem-solving and creativity.
- Water increases the neurotransmitters dopamine, sometimes called the feel-good hormone; serotonin, also known as the happiness hormone; and oxytocin, described as the cuddle hormone; and decreases cortisol, described as the stress hormone.
- Water is a source of awe that expands a person’s compassion.
- The color, sound and feel of water can lower pulse rate and increase feelings of calmness.
The blue mind effect can be achieved by swimming, bathing or even drinking a glass can even help you reach this state. One study even found that observing an aquarium for at least 10 minutes can significantly lower blood pressure and heart rate.
Swimming or bathing to experience the Blue Mind Theory
Swimming can have an effect similar to doing yoga, as the deep breathing, gentle movement and stretching all combine to put a person in that mild meditative state.
Immersing in water levels out the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, which, respectively, control the “fight or flight” response during a threat or perceived danger and the “rest and digest” mode, restoring the body to a state of calm.
Can drinking a glass of water help me achieve the Blue Mind effect?
Even mild dehydration can have negative effects on a body’s ability to function properly, resulting in higher levels of anxiety and fatigue, while decreasing reaction time and overall ability to focus. Because water is the major component of most body parts, there are many reasons to stay hydrated, including:
- Forming saliva for digestion.
- Keeping mucosal membranes moist.
- Allowing body cells to grow, reproduce and survive.
- Flushing body waste, mainly in the urine.
- Lubricating joints.
- Helping the brain manufacture hormones and neurotransmitters.
- Regulating body temperature (sweating and respiration).
- Acting as a shock absorber for the brain and spinal cord.
- Converting food to components needed for survival through digestion.
- Helping deliver oxygen throughout the body.
Keep reading:
Photo credit: Getty Images





